Ongoing Research and Preliminary Findings
Many cosmic rays are absorbed by the atmosphere, and it is well known that the number of observed cosmic rays increases with altitude. Utilizing this phenomenon, we are conducting experiments at higher altitudes to confirm that cosmic rays can indeed be detected using CMOS camera image sensors.
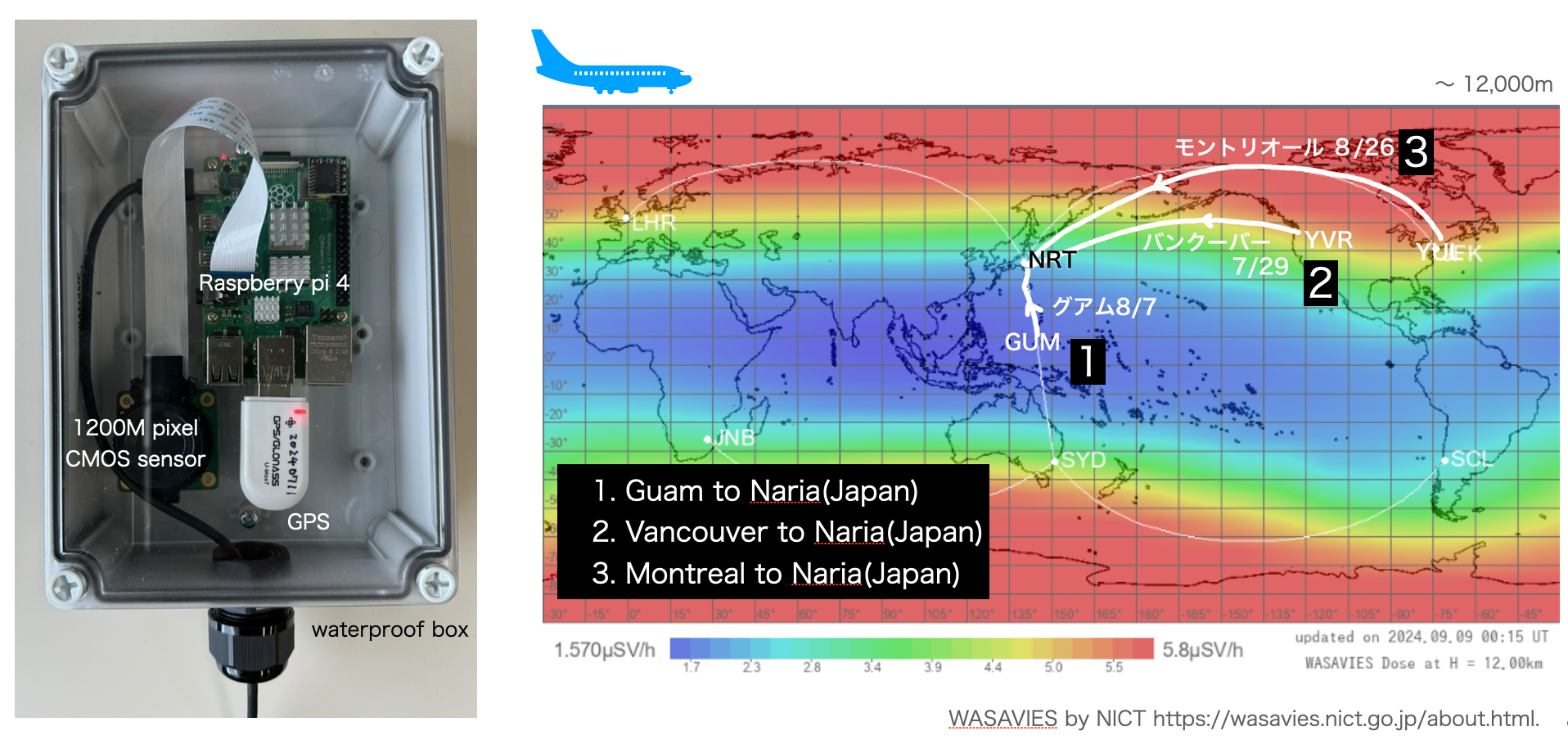
We prepared a detector similar to the one shown on the left and conducted experiments on an airplane. A CMOS sensor is connected to a Raspberry Pi, and the white device is a GPS housed in a waterproof box.
The flight routes consist of three options: Guam, Vancouver, and Montreal, all flying to Japan. As shown in the color-coded diagram, there is a significant difference in cutoff rigidity due to the magnetic field for the Guam route. Therefore, if observations are successful, we anticipate a noticeable difference in the increase in observation amounts.
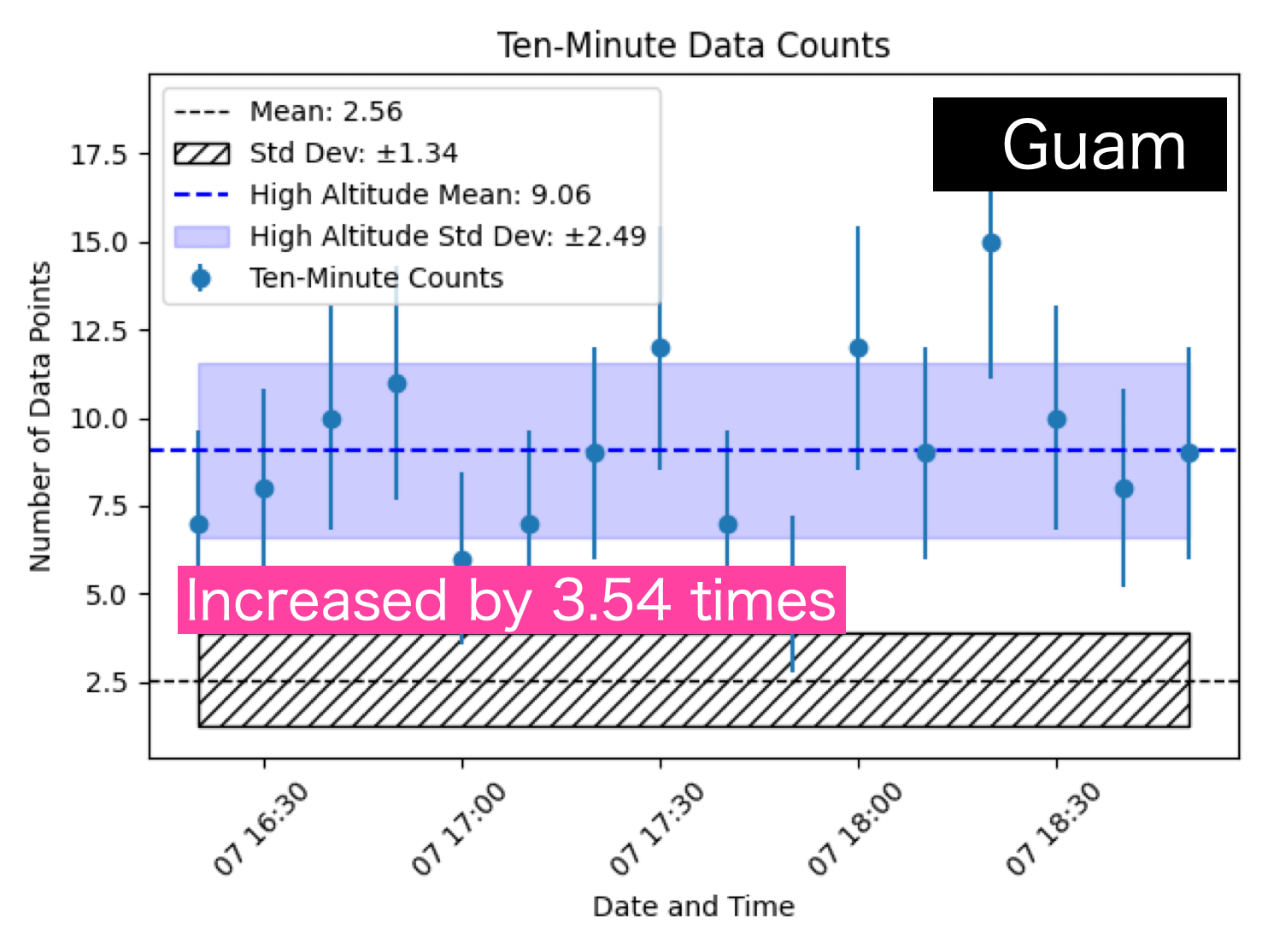
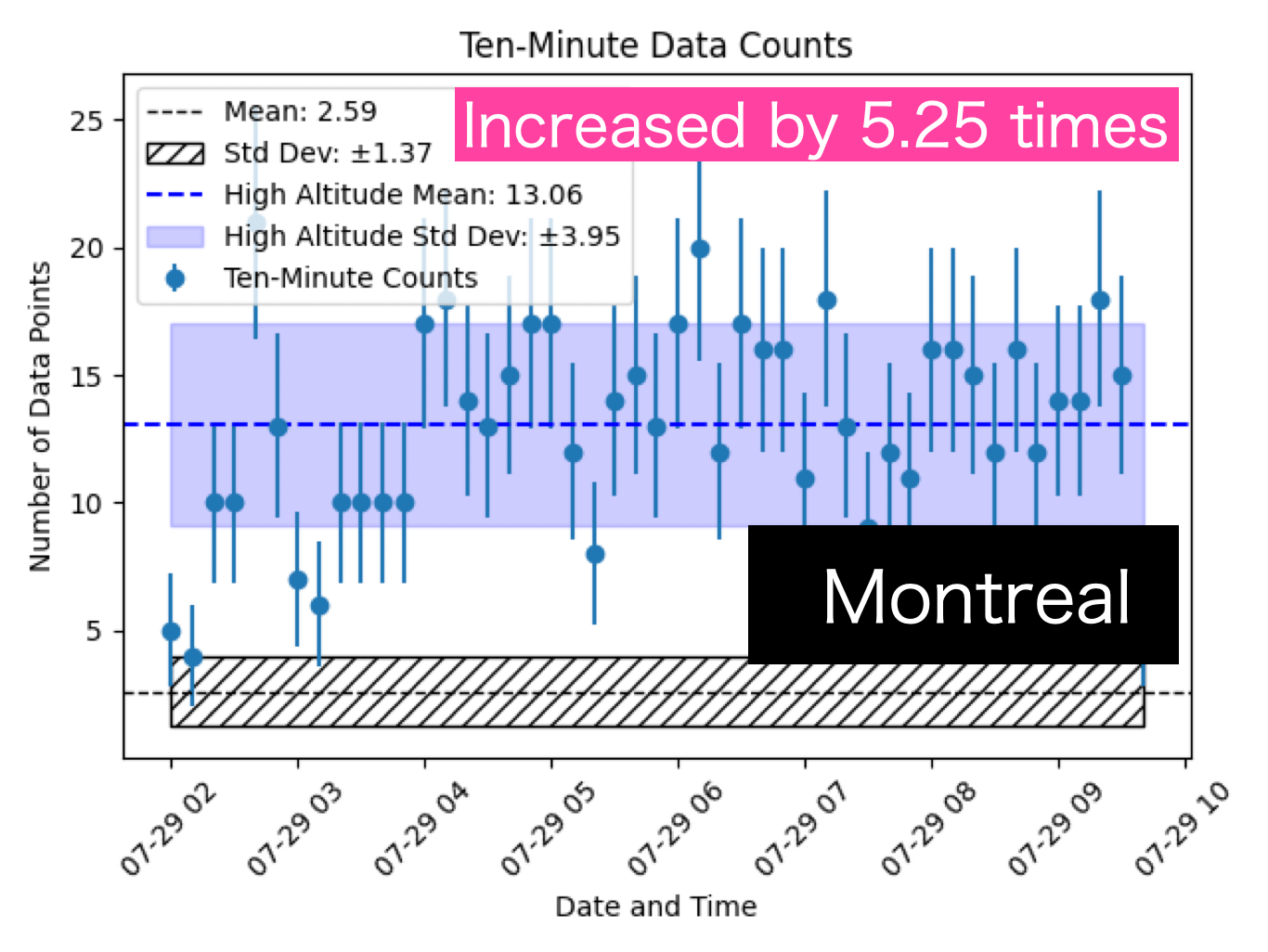
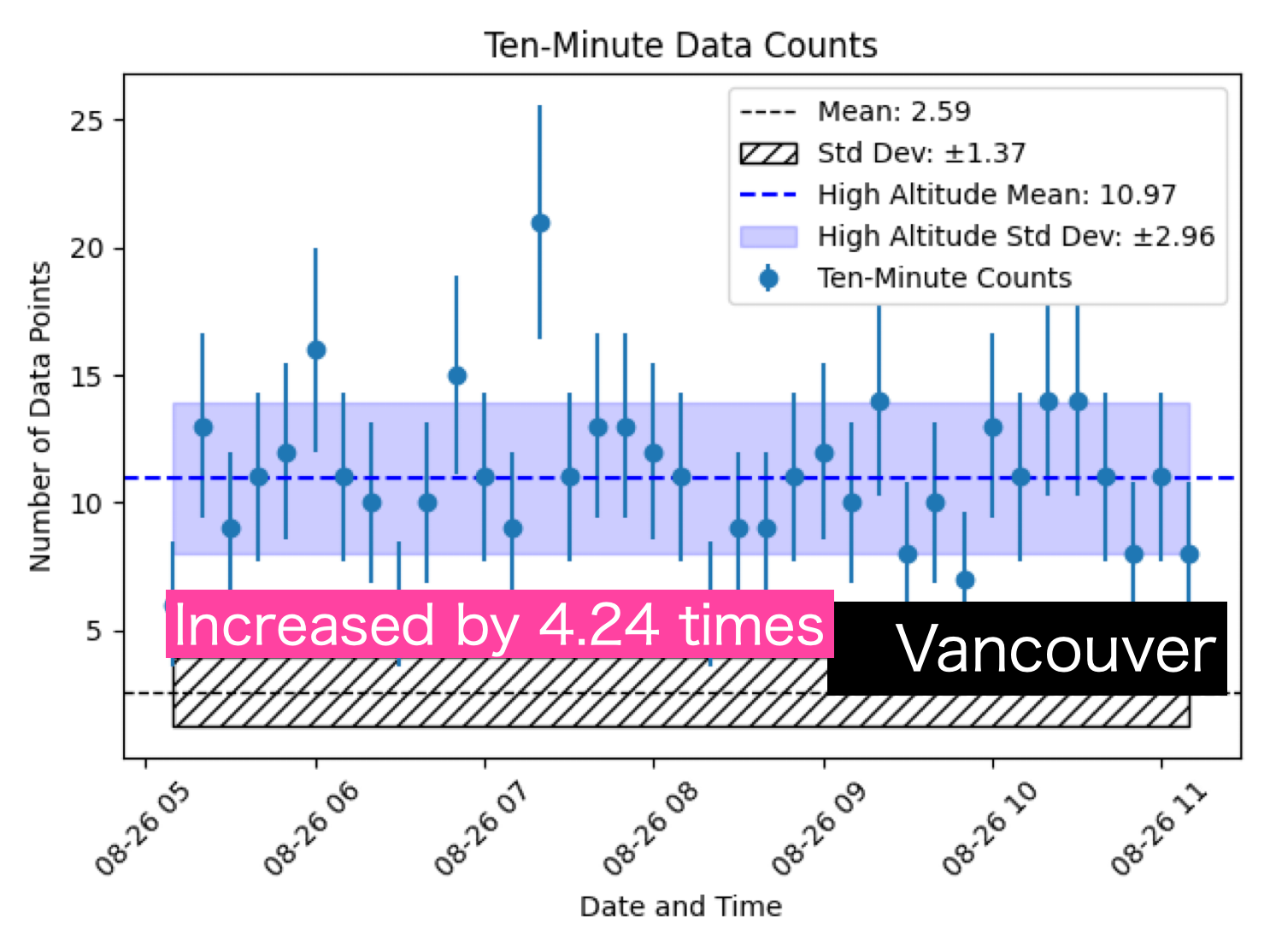
The three figures below represent actual observation results. The shaded areas indicate the average signal levels and standard deviations from ground observations.
In the Guam route, we have extracted the time periods with sufficiently increased observation levels, displaying the average and standard deviation. From this, we can see an increase of 3.54 times compared to ground levels. Similarly, the Vancouver route shows a 4.24 times increase, while the Montreal route shows a 5.25 times increase.
As predicted, the Guam route, which experiences the strongest cutoff due to the magnetic field, has the least increase.
Other comparative Measurements
- Comparative Measurements Between Airplane and Ground (iPad Air 3rd Generation)
- Comparative Measurements Between Airplane and Ground (RaspberryPi + HQ camera)
Peer-reviewed papers
- Development of a Smartphone-Based Radiation Detection App and Its Application to Science Education Outreach: New Possibilities for Science Education Through a Cosmic Ray Detection App
Conference Presentations
-
SORAMAME: Scientific Observation & Research on Astroparticles—Anywhere, by Anyone Presentation slide -
Observations of Ultra High-Energy Cosmic Ray Air Showers using CMOS Camera Image Sensors (6) -
Development of a Smartphone-Based Radiation Detection App and Its Application to Science Education Outreach – New Possibilities for Science Education Through a Cosmic Ray Detection App PoS ICRC2025 (2025) 1255 -
Observations of Ultra High-Energy Cosmic Ray Air Showers using CMOS Camera Image Sensors (5) -
Observations of Ultra High-Energy Cosmic Ray Air Showers using CMOS Camera Image Sensors (4) -
A New Method for Observing the Core of the Highest Energy Cosmic Rays Using Compact Detectors. PoS(ICRC2023)410Consumer Devices with CMOS camera image sensors as Pocket-Sized Particle Detectors. PoS(ICRC2023)1620 -
Observations of Ultra High-Energy Cosmic Ray Air Showers using CMOS Camera Image Sensors - Proposal of a Simple Observation Model Performing Observations with Three CMOS Sensors as an Array and iOS App 'Soramame' -
Observations of Ultra High-Energy Cosmic Ray Air Showers using CMOS Camera Image Sensors (3) -
Observing Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays EAS Core using CMOS Camera Image Sensors -
Observations of Ultra High-Energy Cosmic Ray Air Showers using CMOS Camera Image Sensors (2) -
Observing Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays EAS Core using CMOS Camera Image Sensors -
Observations of Ultra High-Energy Cosmic Ray Air Showers using CMOS Camera Image Sensors